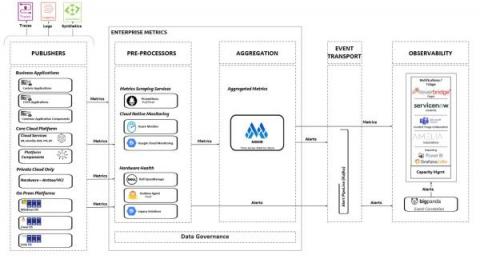
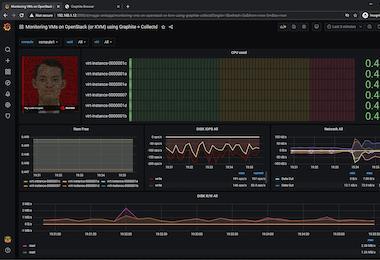
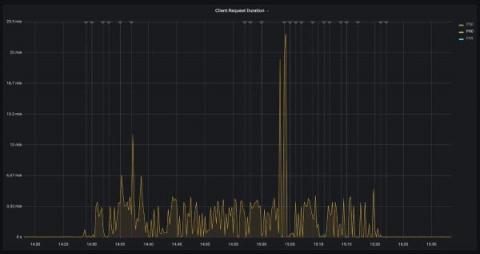
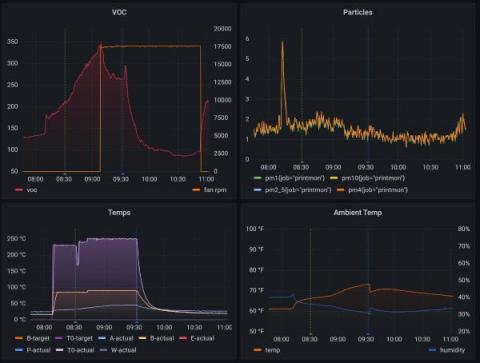
Grafana 9.4 release: Easy data source setup, custom panels, Grafana Alerting updates, and more
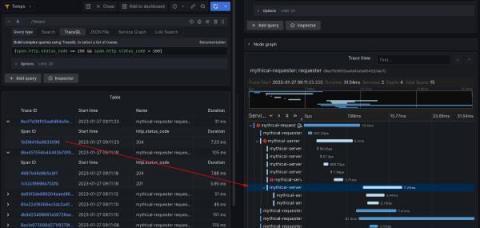
Grafana 9.4 is here! Get Grafana 9.4 With the latest Grafana release, we’re introducing a wealth of new features and improvements that makes getting started with Grafana even easier and that take your visualizations and observability best practices to the next level. In addition to enabling TraceQL, the new query language for distributed tracing in Grafana Tempo 2.0, for all Grafana Cloud users, the Grafana 9.4 release comes with a fresh round of features.