Running LogicMonitor API Scripts in AWS Lambda
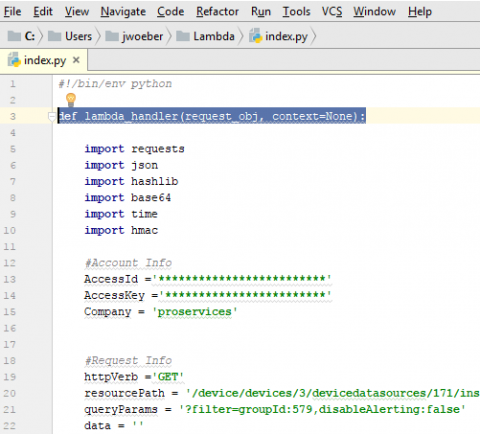
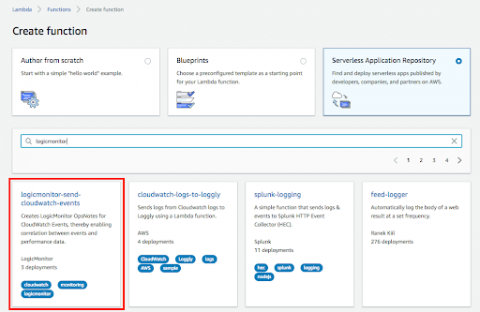
Sometimes it's necessary to run a maintenance API script in your LogicMonitor portal. For example, I move decommissioned devices into a specific folder because I no longer want to receive any alerts on these devices. An API script helps automate the process by running once a day to disable alerts on any new devices added to this folder.